이번에는 안드로이드의 input (터치, 제스처 등)을 관리하는 inputManager에 대해서 알아보려고 합니다
inputflinger의 시작은 init.rc가 시작 되는 시점에 inputflinger.rc가 시작 됩니다
// inputflinger.rc
service inputflinger /system/bin/inputflinger
class main
user system
group input wakelock
# onrestart restart zygote
InputFlinger로 빌드 되어 있는 main.cpp가 시작되고 아래의 코드 순서대로 호출이 됩니다
여기서 봐야할 부분은InputDriver에서 input_open을 호출해주는 부분입니다
// main.cpp
int main(int, char**) {
ProcessState::self()->setThreadPoolMaxThreadCount(4);
BinderService<InputFlinger>::publishAndJoinThreadPool(true); // inputflinger 생성 및 service에 추가
return 0;
}
// inputflinger.cpp
InputFlinger::InputFlinger() :
BnInputFlinger() {
ALOGI("InputFlinger is starting");
mHost = new InputHost();
mHost->registerInputDriver(new InputDriver(INPUT_INSTANCE_EVDEV));
}
// inputDriver.cpp
InputDriver::InputDriver(const char* name) : mName(String8(name)) {
const hw_module_t* module;
int err = input_open(&module, name);
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(err != 0, "Input module %s not found", name);
mHal = reinterpret_cast<const input_module_t*>(module);
}
// input.h
static inline int input_open(const struct hw_module_t** module, const char* type) {
return hw_get_module_by_class(INPUT_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, type, module);
}
// hardware.c
int hw_get_module_by_class(const char *class_id, const char *inst,
const struct hw_module_t **module)
...
snprintf(prop_name, sizeof(prop_name), "ro.hardware.%s", name);
if (property_get(prop_name, prop, NULL) > 0) {
if (hw_module_exists(path, sizeof(path), name, prop) == 0) {
goto found;
}
}
/* Loop through the configuration variants looking for a module */
for (i=0 ; i<HAL_VARIANT_KEYS_COUNT; i++) {
if (property_get(variant_keys[i], prop, NULL) == 0) {
continue;
}
if (hw_module_exists(path, sizeof(path), name, prop) == 0) {
goto found;
}
}
/* Nothing found, try the default */
if (hw_module_exists(path, sizeof(path), name, "default") == 0) {
goto found;
}
return -ENOENT;
found:
/* load the module, if this fails, we're doomed, and we should not try
* to load a different variant. */
return load(class_id, path, module);
}
input_open을 호출해주면 hw_get_module_by_class를 통해서 "input" 이라는 이름의 module을 찾는데
/system/lib/hw, /vendor/lib/hw (64비트면 lib64) path에 라이브러리가 있으면 동적으로 로딩을 해주는 식입니다
// hardware/libhardware/hardware.c
#if defined(__LP64__)
#define HAL_LIBRARY_PATH1 "/system/lib64/hw"
#define HAL_LIBRARY_PATH2 "/vendor/lib64/hw"
#else
#define HAL_LIBRARY_PATH1 "/system/lib/hw"
#define HAL_LIBRARY_PATH2 "/vendor/lib/hw"
#endif
static int hw_module_exists(char *path, size_t path_len, const char *name,
const char *subname)
{
snprintf(path, path_len, "%s/%s.%s.so",
HAL_LIBRARY_PATH2, name, subname);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)
return 0;
snprintf(path, path_len, "%s/%s.%s.so",
HAL_LIBRARY_PATH1, name, subname);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0)
return 0;
return -ENOENT;
}
// hardware/libhardware/hardware.c
static int load(const char *id,
const char *path,
const struct hw_module_t **pHmi)
{
...
handle = dlopen(path, RTLD_NOW);
const char *sym = HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM_AS_STR;
hmi = (struct hw_module_t *)dlsym(handle, sym);
...
hmi->dso = handle;
/* success */
status = 0;
...
*pHmi = hmi;결국 동적으로 붙은 module을 전달하며, 그 모듈을 mHal로 저장해둡니다 (Hardware Abstract Layer)
inputDriver는 결국 lib단에서 inputFlinger host 단으로 호출될 수 있도록 kCallback을 넘겨줍니다
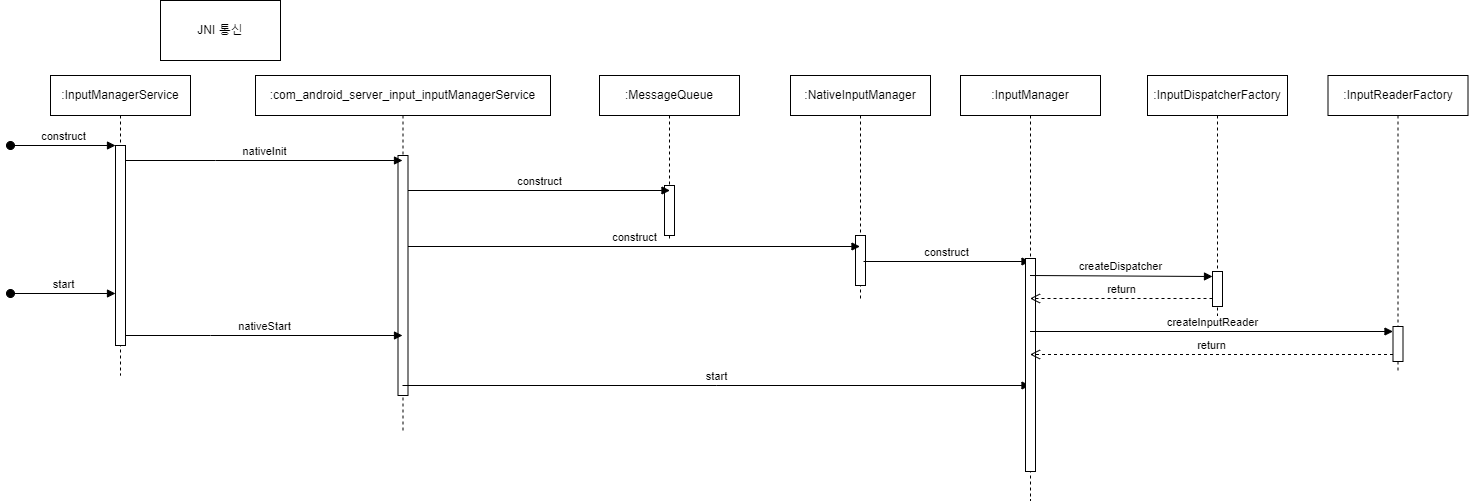
여느 service들과 마찬가지로 InputManagerService 또한 SystemServer 내에서 시작됩니다
// SystemServer.java
private void startOtherServices(@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) {
...
InputManagerService inputManager = null;
...
t.traceBegin("StartInputManagerService");
inputManager = new InputManagerService(context);
t.traceEnd();
...
t.traceBegin("StartInputManager");
inputManager.setWindowManagerCallbacks(wm.getInputManagerCallback());
inputManager.start();
'안드로이드 > 안드로이드 프레임워크' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 안드로이드 앱 프레임워크 학습(ActivityManager) 3 (2) | 2024.03.10 |
|---|---|
| 안드로이드 앱 프레임워크 학습(ActivityManager) 2 (2) | 2024.03.03 |
| 안드로이드 앱 프레임워크 학습(ActivityManager) 1 (2) | 2024.03.01 |
| 안드로이드 앱 프레임워크 학습(WindowManager) 3 (1) | 2024.03.01 |
| 안드로이드 앱 프레임워크 학습(WindowManager) 2 (3) | 2024.02.29 |